Linear bearings are essential components in many machines and mechanical systems. They play a critical role in achieving smooth and precise linear motion. These bearings are designed to convert rotary motion into linear movement, improving efficiency and accuracy in various applications. In this guide, we’ll explain what a linear bearing is, how it works, and its key types and uses.
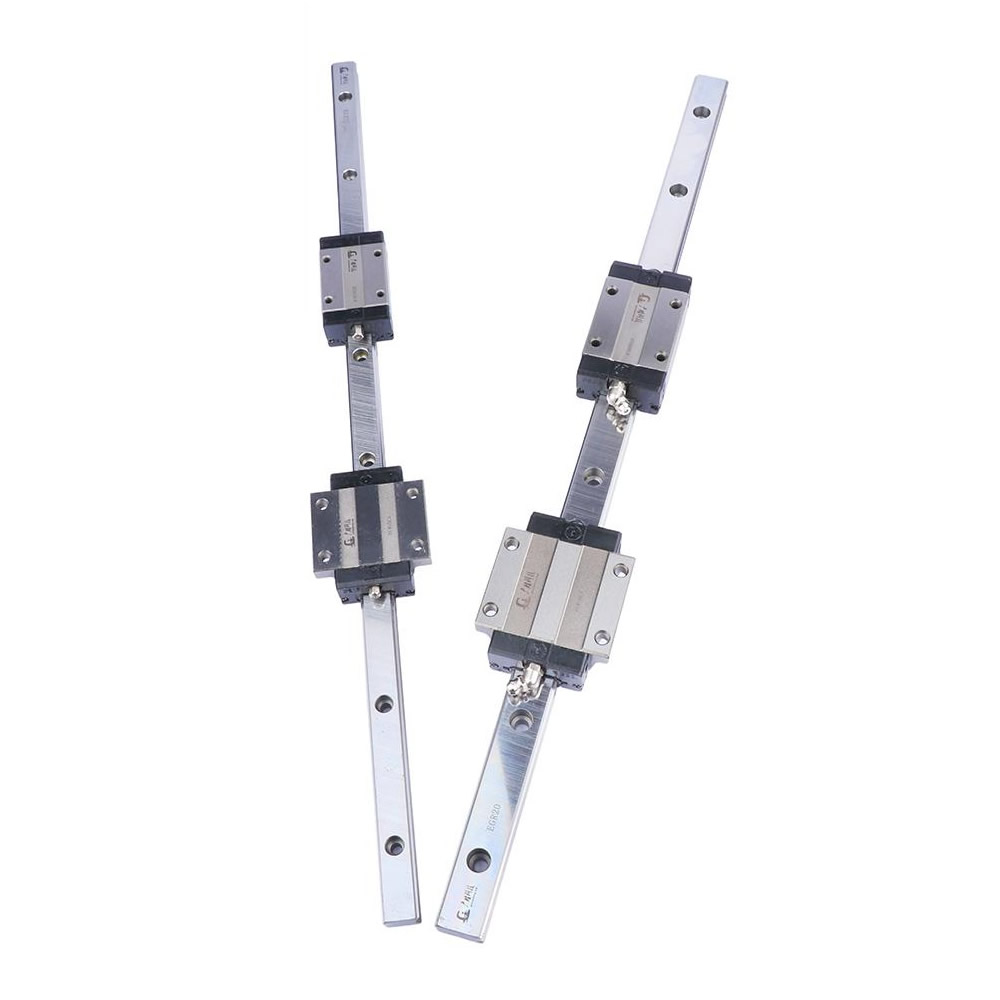
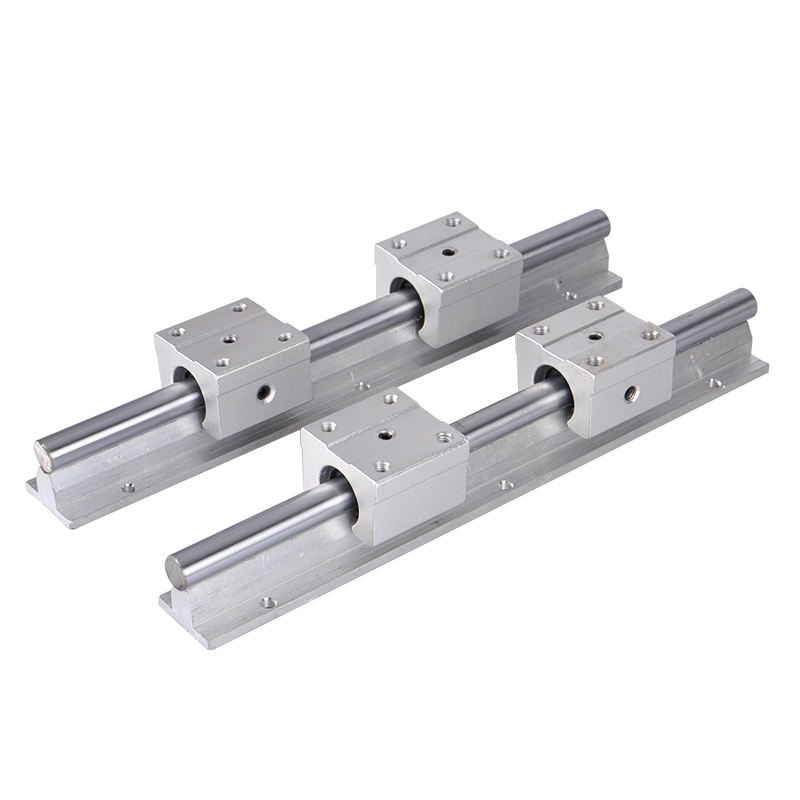
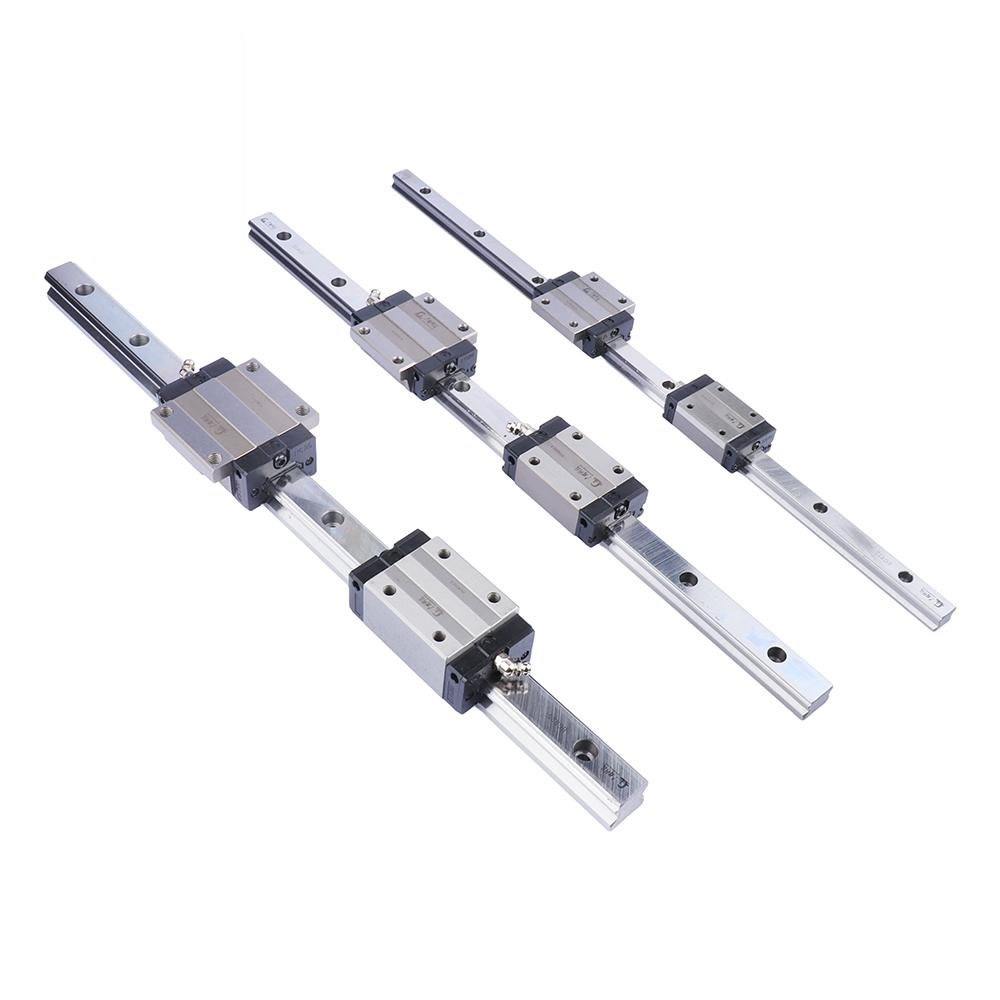
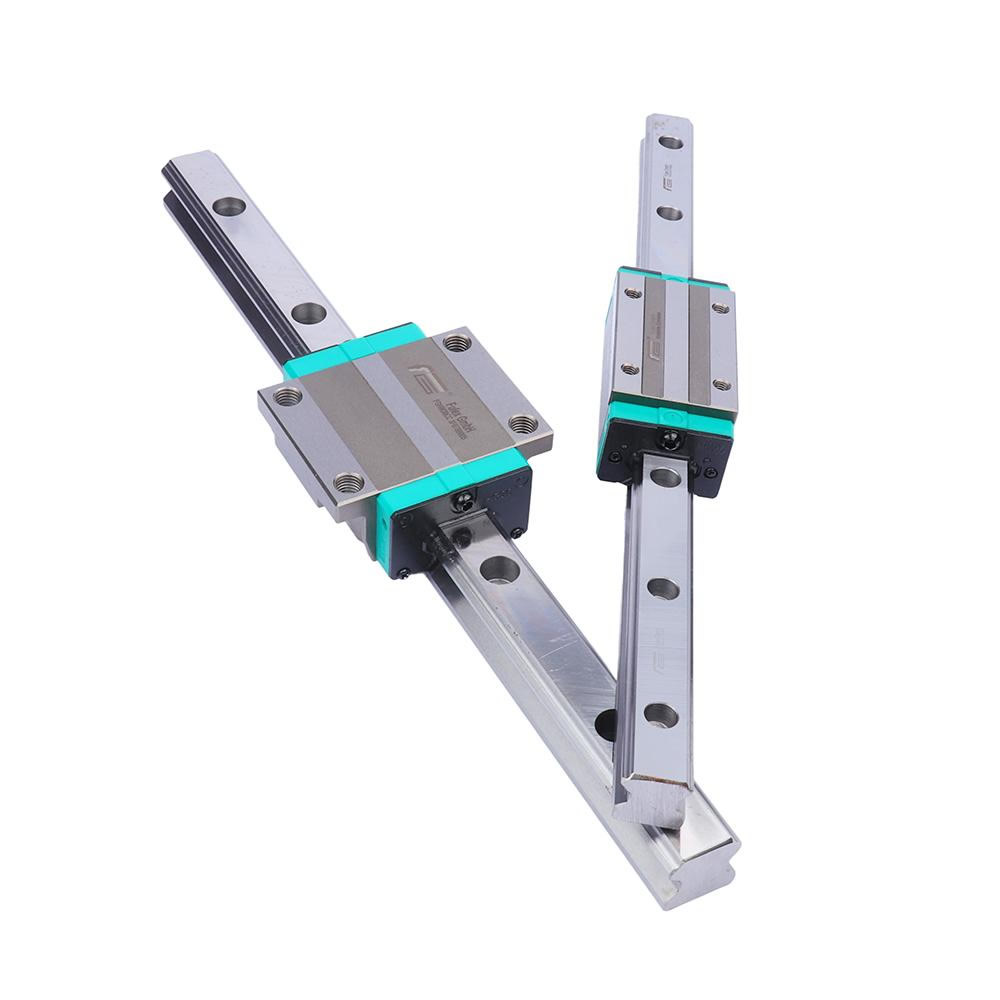
A linear bearing aims to work with the linear rail or guide shaft to provide low friction movement in a single direction while “bearing” the load. Linear bearings are part of linear motion systems in many industries and applications.
Types of Linear Bearings
Several types of linear bearings can be used within a linear motion system. When building your system, you will need to look at your needs to determine which bearing is best for your application.
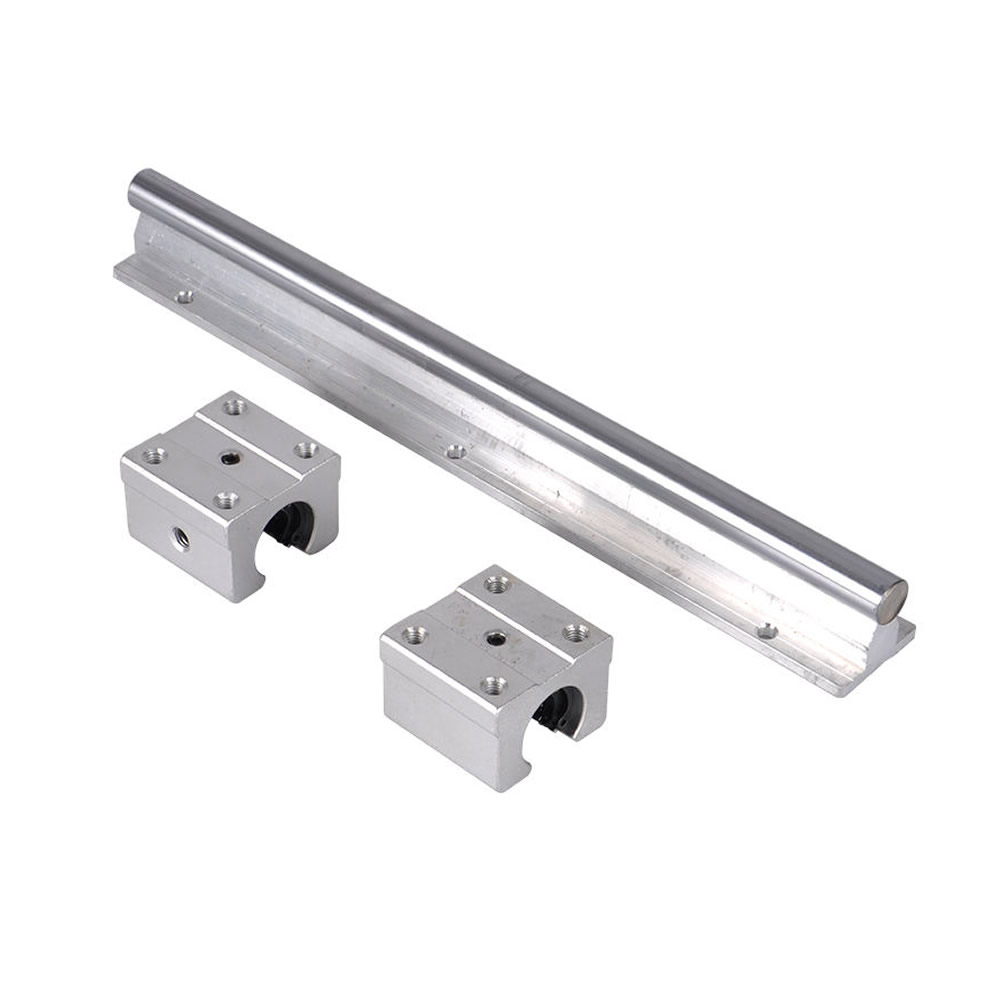
- Linear Rails or Guides: These provide the track for the bearing to move along, ensuring smooth and controlled linear motion.
- Carriages: Carriages hold the bearings and move along the rails. They distribute the load and connect the bearing to the moving object.
- Drive Mechanisms: Belts, screws, or lead screws convert rotary motion into linear movement, driving the system efficiently.
- Linear Motors: Directly generate linear motion without traditional mechanisms, offering efficient force for certain applications.
- Support Structures: Frames and brackets stabilize the entire system, keeping it aligned and supporting the load.
- End Supports: These maintain the rail alignment and prevent lateral movement, adding stability to the system.
- Encoders and Sensors: Provide feedback on position and speed, essential for precision control and accuracy.
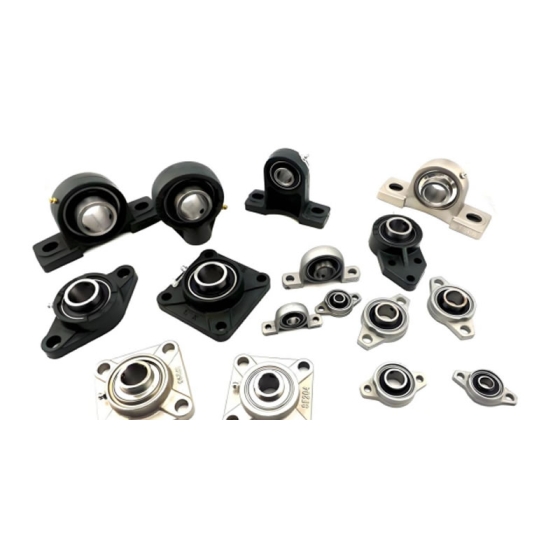
- Bearing Housing or Blocks: Protect the bearings and enhance durability while offering stable support.
- Seals and Lubrication: Protect bearings from debris and reduce friction, ensuring smooth operation and longevity.
- Mounting Hardware: Bolts and fasteners secure the components, ensuring stability and safe operation.
- Controllers and Electronics: Manage the motion and provide commands to the drive mechanisms, critical in automated systems.
- Power Supply: Provides energy to drive mechanisms and electronics, ensuring continuous operation.
These components work together to create a smooth, efficient, and precise linear motion system tailored to various industrial needs.
 Shandong Bard Bearing Co., Ltd.
Shandong Bard Bearing Co., Ltd.